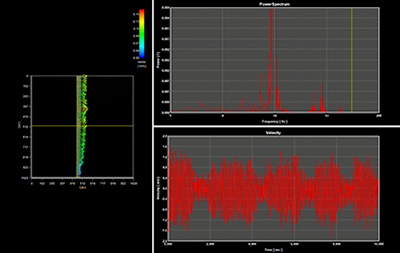
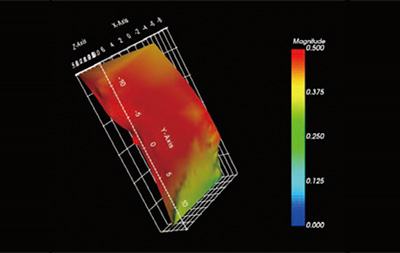
- SEIKA Digital Image Corporation.
- Measurement
- DIC: Digital Image Correlation Strain analysis
DIC: Digital Image Correlation Strain analysis
Digital Image Correlation
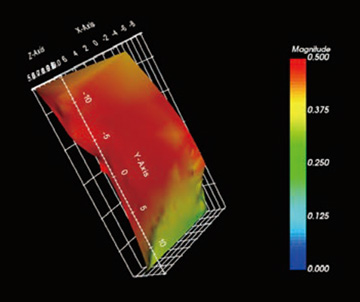
DIC (Digital Image Correlation) analyzes the degree of deformation by analyzing the image before and after sample deformation. Not only the deformation amount but also the deformed direction can be detected. By using this system, it is possible to quantify the distortion and deformation of an object in non-contact and non-destructive manner. By using a high-speed camera, analysis of high-speed phenomena and vibration is also possible.
Digital image
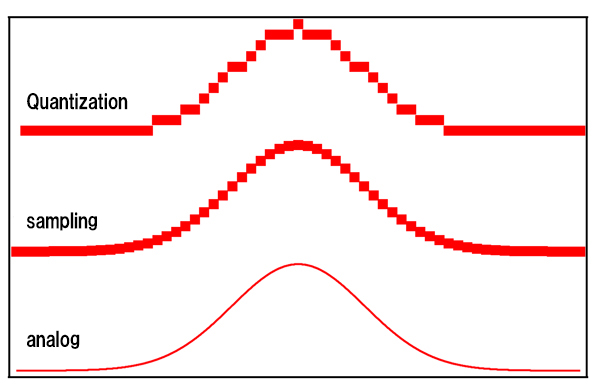
A digital image consists of a collection of pixels. In addition, the luminance value (brightness information) of each pixel is quantized and takes a discrete value. Such a digital image is often made by photographing the subject using an image sensor in many cases. The brightness value of the subject is sampled for each pixel of the image sensor and then quantized by the A / D converter.In this process, information between pixels and quantized luminance value and luminance value is lost. This figure is a schematic representation of how the information of one line of the subject changes with sampling and quantization. The information of the subject is smooth like a line with analog display, but after sampling and quantization it gets a discrete value and some information is lost. The fineness of sampling is determined by the number of pixels, and the granularity of quantization is determined by the bit depth. Because it happens when acquiring digital images, you need to decide to consider the parameters carefully when shooting.
Speckle pattern
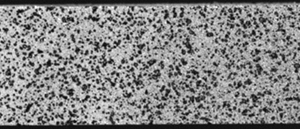
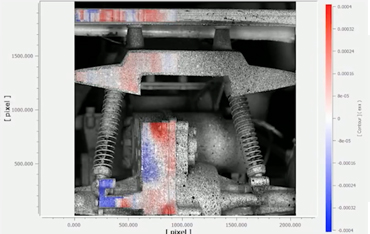
The random pattern as shown in the figure is called speckle pattern. In the digital image correlation method, it is possible to measure deformation and distortion of a subject with high resolution by constructing a speckle pattern on the subject's surface. To construct speckle patterns, there are various methods such as painting and spraying of minute substances.
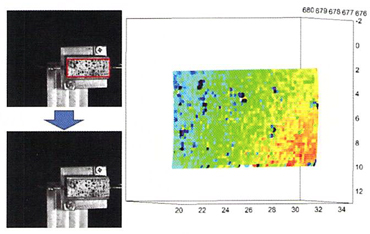
Subset
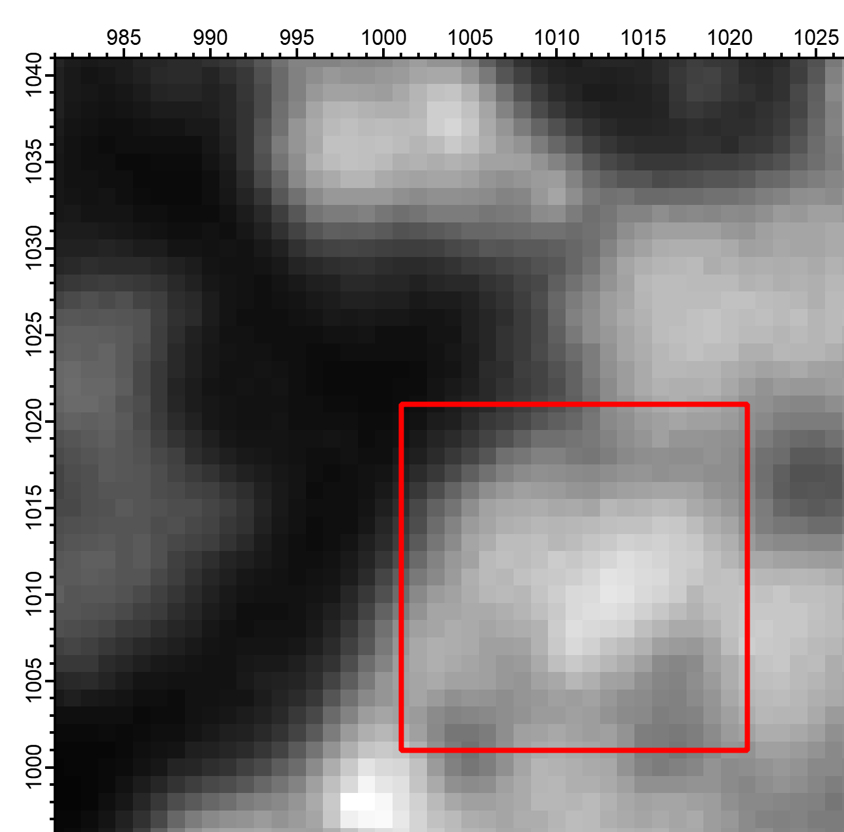

In the digital image correlation method, as shown in the red frame in the figure, the subject is divided into a minute area called a subset. Each subset is the measurement point. Calculate deformation and strain by measuring the displacement amount of the subset.
Features
- Measure coordinate, displacement,velocity, strain, shape and deformation
- Vector diagram / Contour diagram
- Supported image format: TIFF etc.
- Easy to use and intuitive interface
- Offline analysis, Online analysis(Optional) 3D analysis(Optional)
- Process tree structure
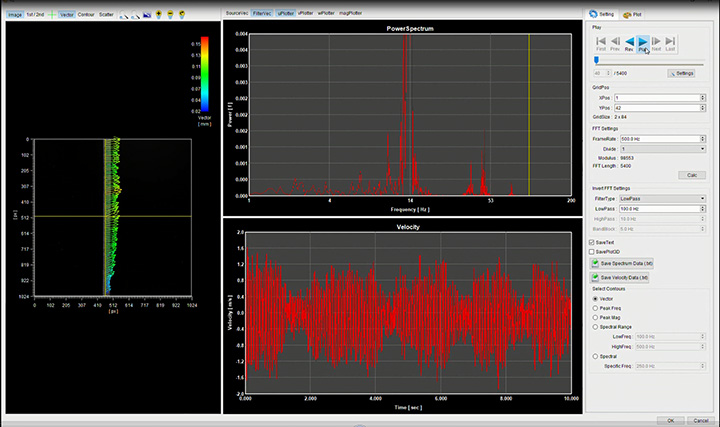
- Various post processing functions (FFT analysis, POD analysis, etc.)
- Supporting various high speed cameras and high resolution cameras
- Japanese and English available
Movie
sDIC digital image correlation method strain measurement system.
It is a case introduction video by sDIC software.
It is a case introduction video (Chinese narration) by sDIC software.
Related products Laser Doppler Vibrometer is an introduction.
Application
- Tension, Compression, Torsion, Vibration Test
- Thermal expansion / thermal deformation
- Destruction · Impact · Drop test
- Micro test by electron microscope
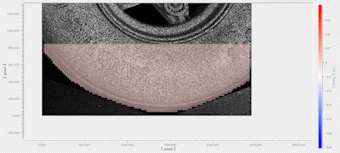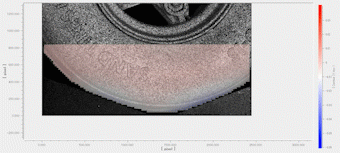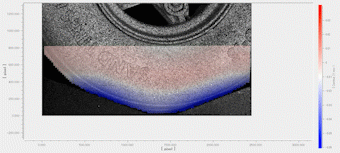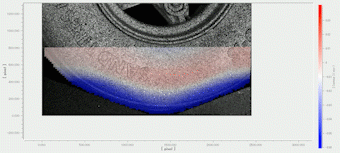
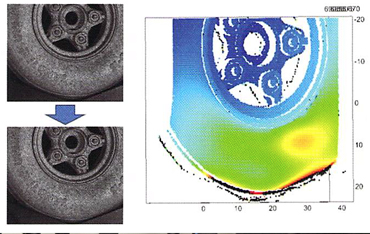
Measurement example
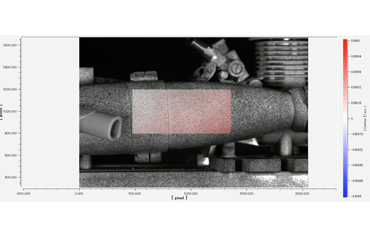
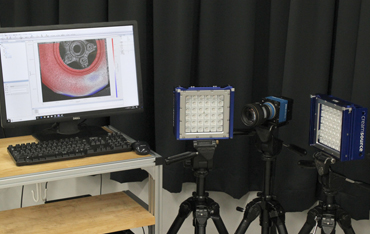
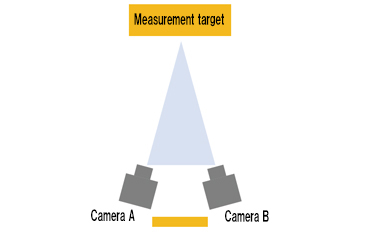
System configuration example
System variation
Standard model specification
| 2D | 3D(stereo) | |
| System configuration | ||
| camera | One | Two |
| illumination | 2 lights | 3 lights |
| Software | sDIC(2D) | sDIC(3D) |
| Calibration target | × | 〇 |
| tripod | 3 sets | 4 sets |
| Camera mount | 〇 | |
| Control PC | 1 set | 1 set |
| Camera | ||
| format | 2/3 inch | |
| resolution | 2,448 × 2,048 pixels | |
| Dynamic range | 12 bit monochrome | |
| Maximum frame rate | 23fps | |
| shutter | global | |
| Connection interface | Ethernet (1000BASE-T) | |
| Applicable lens | C-Mount/F-Mount | |
| Illumination | ||
| method | LED | |
| Color temperature | 2700-6500°K | |
| Maximum illuminance | 55,100lx(6500°K) | |
| Beam angle | 13° | |
| Control PC | ||
| OS | windows 10PRO For Workstation | |
| processor | Intel Xeon processor (4 cores) | |
| memory | 32GB DDR-4 SDRAM | |
| storage | 512 GB M.2 slot SSD 2 TB hard disk drive | |
| monitor | 24 inch wide monitor | |
| Software specification | ||
| Image format | tiff | |
| Image correction | ○ (Gaussian filter) | |
| Mask · ROI | 〇 | |
| display | 2D | 3D |
| Measurement item | Shape, deformation, various strain | |
| Calculation precision | 1/100 pixels or less | 1/100 pixels or less (in-plane direction) 1/50 pixels or less (out-of-plane direction) |
Contact
Any inquiry or request for information, please click here.